We present high-resolution (0![]() 3) Atacama Large Millimeter Array 870 μm imaging of 52 sub-millimeter galaxies (SMGs) in the Ultra Deep Survey field to investigate the size and morphology of the sub-millimeter (sub-mm) emission on 2-10 kpc scales. We derive a median intrinsic angular size of FWHM = 0
3) Atacama Large Millimeter Array 870 μm imaging of 52 sub-millimeter galaxies (SMGs) in the Ultra Deep Survey field to investigate the size and morphology of the sub-millimeter (sub-mm) emission on 2-10 kpc scales. We derive a median intrinsic angular size of FWHM = 0![]() 30 ± 0
30 ± 0![]() 04 for the 23 SMGs in the sample detected at a signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) >10. Using the photometric redshifts of the SMGs we show that this corresponds to a median physical half-light diameter of 2.4 ± 0.2 kpc. A stacking analysis of the SMGs detected at S/N <10 shows they have sizes consistent with the 870 μm bright SMGs in the sample. We compare our results to the sizes of SMGs derived from other multi-wavelength studies, and show that the rest-frame ~250 μm sizes of SMGs are consistent with studies of resolved 12CO (J = 3-2 to 7-6) emission lines, but that sizes derived from 1.4 GHz imaging appear to be approximately two times larger on average, which we attribute to cosmic ray diffusion. The rest-frame optical sizes of SMGs are around four times larger than the sub-millimeter sizes, indicating that the star formation in these galaxies is compact relative to the pre-existing stellar distribution. The size of the starburst region in SMGs is consistent with the majority of the star formation occurring in a central region, a few kiloparsecs in extent, with a median star formation rate surface density of 90 ± 30 M ☉ yr–1 kpc–2, which may suggest that we are witnessing an intense period of bulge growth in these galaxies.
04 for the 23 SMGs in the sample detected at a signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) >10. Using the photometric redshifts of the SMGs we show that this corresponds to a median physical half-light diameter of 2.4 ± 0.2 kpc. A stacking analysis of the SMGs detected at S/N <10 shows they have sizes consistent with the 870 μm bright SMGs in the sample. We compare our results to the sizes of SMGs derived from other multi-wavelength studies, and show that the rest-frame ~250 μm sizes of SMGs are consistent with studies of resolved 12CO (J = 3-2 to 7-6) emission lines, but that sizes derived from 1.4 GHz imaging appear to be approximately two times larger on average, which we attribute to cosmic ray diffusion. The rest-frame optical sizes of SMGs are around four times larger than the sub-millimeter sizes, indicating that the star formation in these galaxies is compact relative to the pre-existing stellar distribution. The size of the starburst region in SMGs is consistent with the majority of the star formation occurring in a central region, a few kiloparsecs in extent, with a median star formation rate surface density of 90 ± 30 M ☉ yr–1 kpc–2, which may suggest that we are witnessing an intense period of bulge growth in these galaxies.
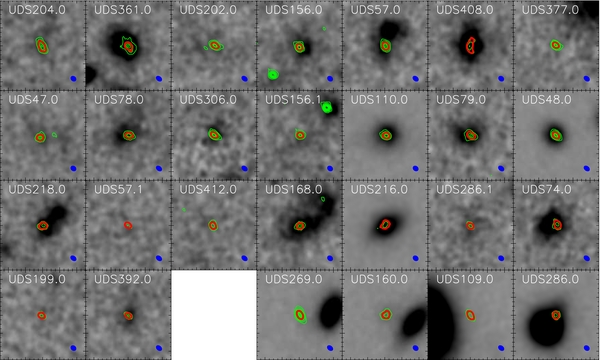
Grayscale K-band images of the 27 bright (S/N > 10σ) ALMA-identified SMGs in our sample. The images are in order of decreasing 870 μm flux density, except for the final four panels, which are classed as potentially lensed SMGs (images are separated by a blank panel). Each panel is 5” × 5” and we contour the ALMA maps over the images of the galaxies. The green contours on each image represent ALMA 870 μm emission at 4, 8, 12, …. × σ, and a single red contour represents where the ALMA 870 μm surface brightness is 50% of the peak value; for an ideal point source this contour should be identical to the size of the ALMA beam FWHM (bottom right of each panel). We note that the red contour appears more extended than the beam, indicating that these SMGs are resolved in the 0farcs3 resolution ALMA data. Overall, 15% of the SMGs are not detected in the K-band imaging (5σ detection limit 25.0 mag).
The full paper can be found in Simpson et al. 2015, ApJ, 799, 81
